Charcot Marie Tooth (CMT)
Introduction

Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) , is inherited peripheral neuropathy affecting the nerves and muscles. It is life-threatening and never affects brain function..Patients with CMT may slowly lose the use of their extremities as nerves degenerate and muscles weaken because the affected nerves can no longer stimulate the muscles. Many patients also present with sensory loss. Since it is hereditary and can be passed down from one generation to the other
Symptoms
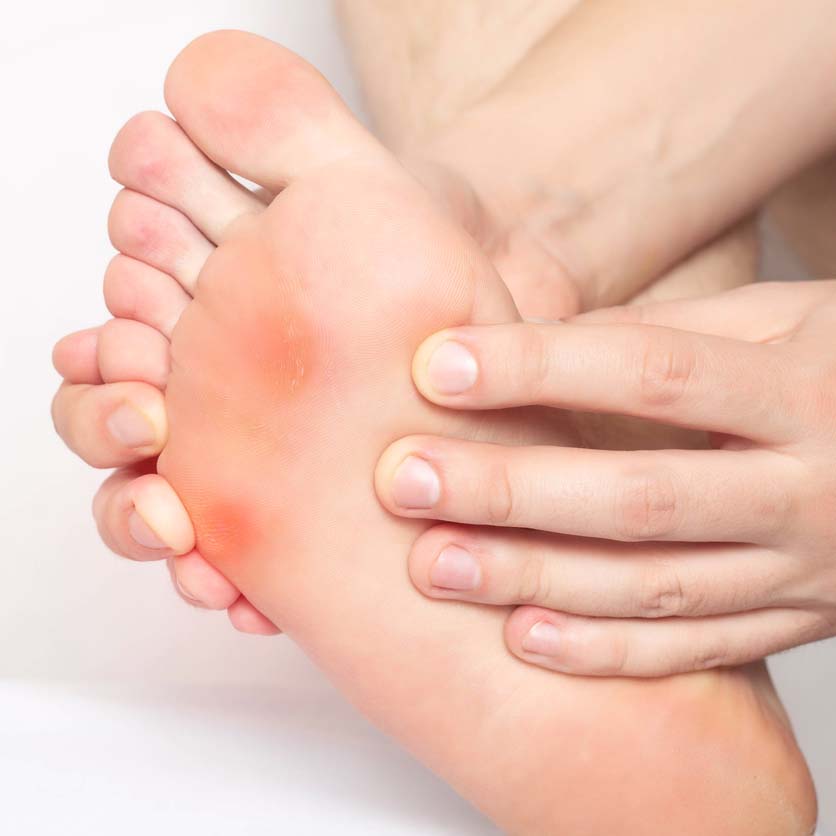
A high arched foot is classically one of the first signs of this disorder, although in some instances flat feet are also typical feature of CMT. As the disease progresses, structural foot deformities may also aggravate. The patient may develop a high-arched foot and hammertoes.
The progressive muscle wasting of CMT leads to difficulties with walking, running, and balance. And many patients develop foot drop.
Later in the stage of the disease, hand function are affected. Tasks requiring fine motor control become difficult. The loss of nerve function is often followed by tingling and burning sensations in the hands and feet..
Investigation
After consulting a Healthcare practitioner, he may refer for Gene studies to identify chromosomal abnormality. Electrodiagnosis such as Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies(NCS) to identify the conduction of nerves. Muscle biopsy will help to detect any change in the structure composition of the muscle.
Treatment and Prevention
There is no cure for CMT at the present time but there are many therapies that CMT patients can benefit from.
Physiotherapy can slow down loss of movement, maintain muscle strength and reduce contractures. Generally patients with CMT should consult a physical therapist to begin aerobic exercises and water based exercise program since it is less strenuous. Incorporating breathing exercises and cardio-respiratory fitness is also crucial. Occupational therapy may help people carry out the tasks of daily living by using assistive devices.
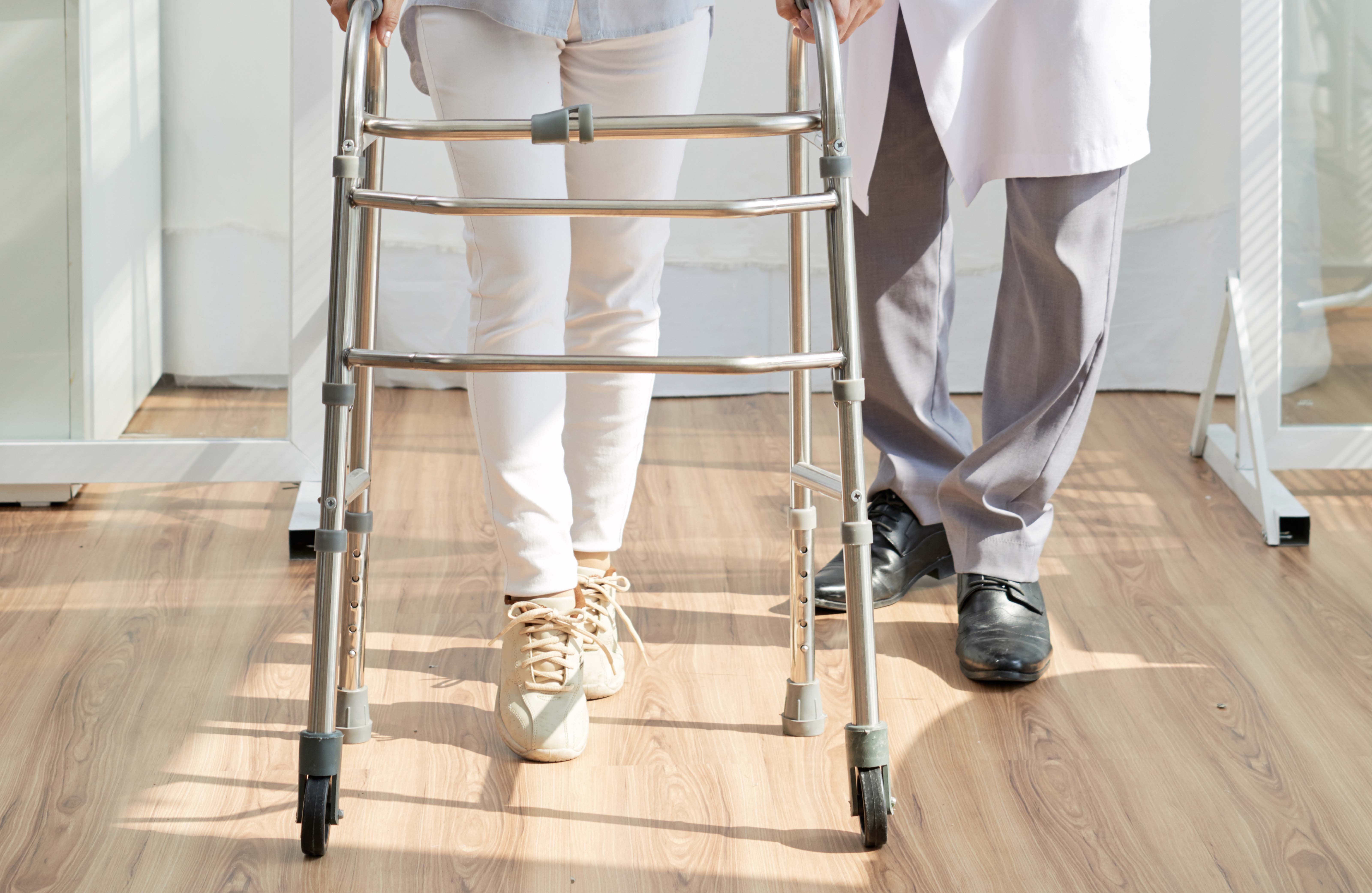

Often walking abnormalities can be corrected by the use of either articulated (hinged) or unarticulated, orthosis called AFOs (ankle-foot orthosis). These orthosis help control foot drop and ankle instability. Walking aids can be prescribed like crutches, walker to prevent risk of fall and keep the patient mobile. It is important for CMT patients to manage their weight, because increased weight makes physical activity more difficult and also increases the stress on relatively compromised joints and muscles. Consulting a counsellor may also benefit to cope up with the disease and gain employment.
Read our Articles