Pregnancy and Your Feet
Introduction
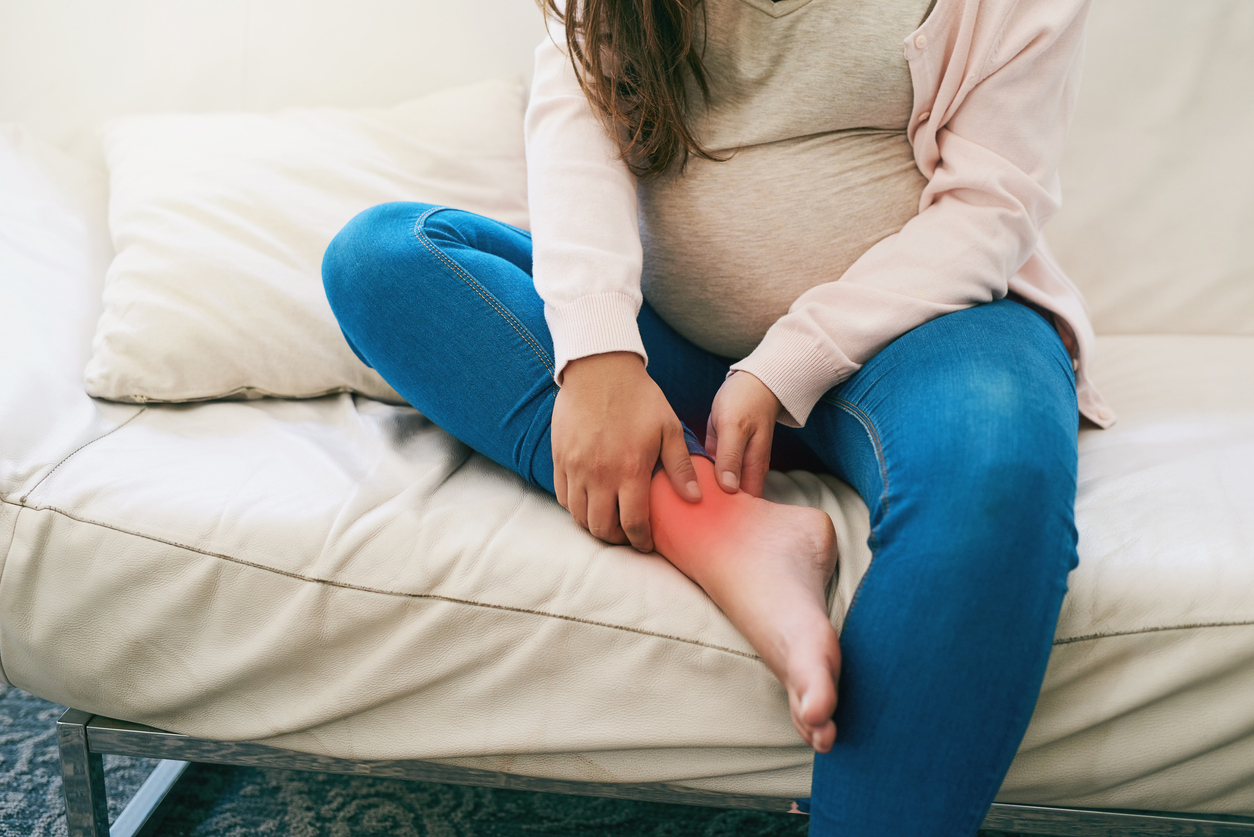

Though Pregnancy is a joyous experience to all expectant mothers, it is responsible to bring about several bodily changes under hormonal influence which impose lifestyle limitations. Pregnancy is a physiological process which sets off many different changes in a woman’s body, of which weight gain is quite remarkable. From the point of view of biomechanics, the heavy uterus pushes the center of gravity forward, exaggerating lumbar lordosis (curves in low back) and affecting the posture and walking pattern, which results in foot and back pain.
During pregnancy, certain hormones cause water retention which increases foot volume, foot pressure, and pain. The foot arches of the pregnant woman tend to collapse during 12 to 34 weeks’ gestation, adopting a flat feet posture. These problems result in heel pain, pain at arch or the ball-of-foot.
Cause
Flat feet and Swelling a very common foot problem experienced during pregnancy.
A flat foot reduces the shock absorbing capacity of the foot and leads to extreme stress on the plantar fascia. A flat foot also makes walking very painful and increases the strain on the feet, calves and/or back. Swelling also referred to as Edema in the feet, normally occurs in the latter stage of pregnancy. Swelling results from the fluid accumulated during pregnancy. The enlarging uterus puts pressure on the blood vessels in the pelvis and legs causing circulation to slow down and blood pools in the legs.
Treatment And Prevention
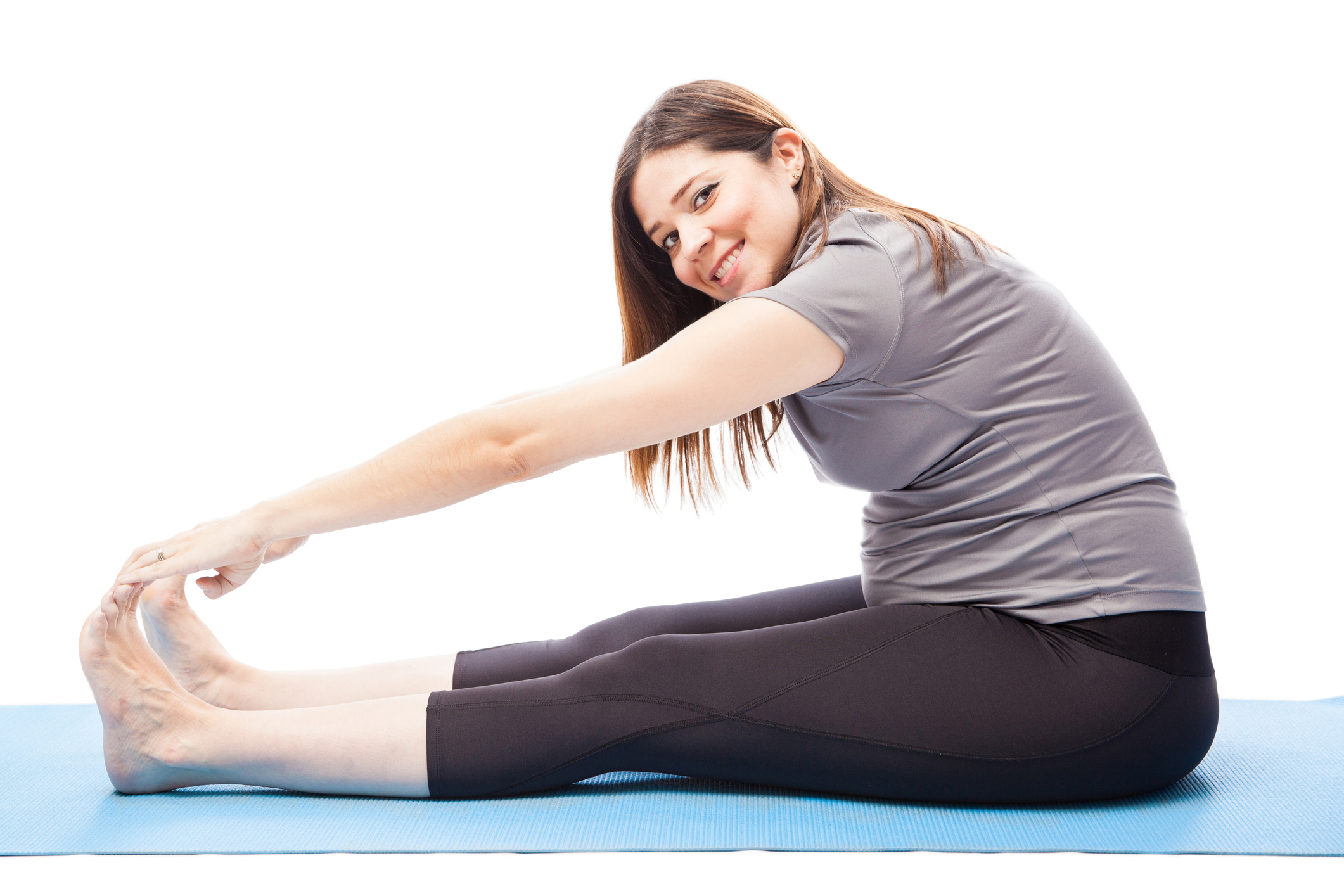

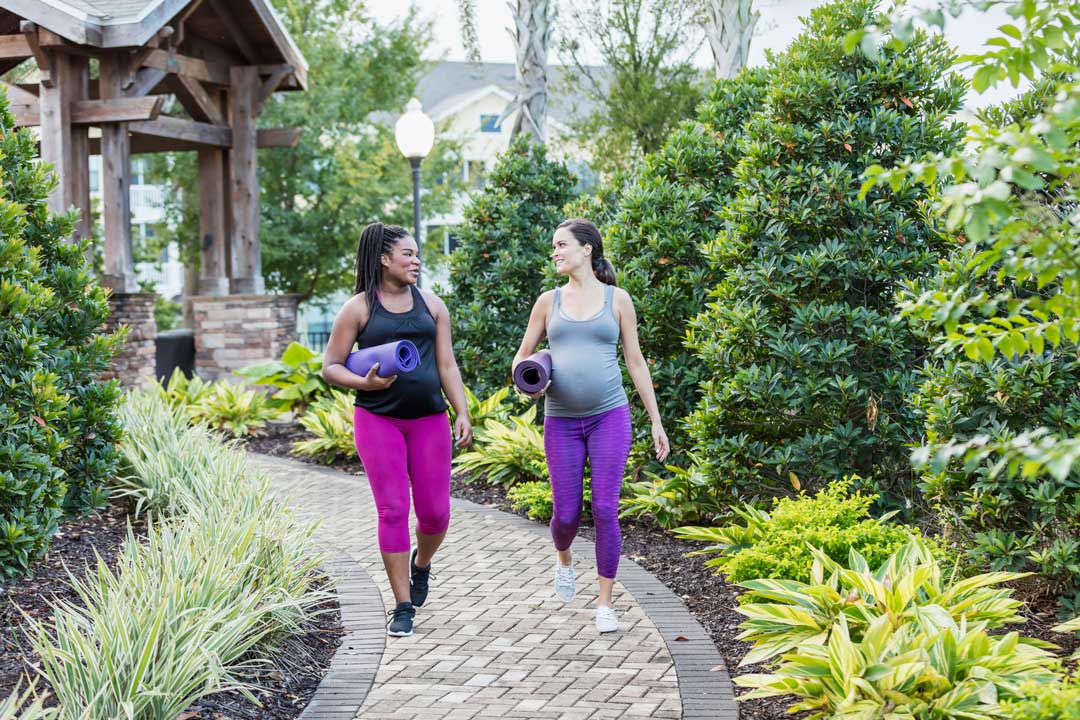
There are effective ways to treat both flat feet and edema during pregnancy. Conservative treatment includes an appropriate arch support and medial rearfoot posting to prevent the over-pronation. Footwear should also be assessed to ensure the fit is proper. Footwear with a firm heel counter is often suggested for extra support and stability.
Exercises for improving the muscle flexibility and reducing arch related pain can be suggested by a Physiotherapist. Edema in the feet can be alleviated by the following methods: Elevate your feet as often as possible. A crepe bandage or compression stockings may help to prevent blood from pooling in the legs. Simple leg movements such as ankle rotations while lying down can also help to reduce the swelling Wear proper fitting footwear. Footwear that is too narrow or short will constrict circulation. A Physiotherapist may help to design antenatal and post natal exercises to reduce the stress of weight gain and stay fit.
Read our Articles