Neuropathy
Definition
According to European Heart Journal Supplements (2015), India ranks second highest with regard to the rising prevalence of diabetes. Diabetic Neuropathy is a devastating and expensive complication of diabetes that affects the nerves. It is the leading cause of non-traumatic foot ulceration and amputation, leading to reduced mobility, falls and poor quality of life. Chief risk factors include age and duration of diabetes yet hypertension, high cholesterol level, and genetic factors are also associated with diabetic neuropathy. The most common type of diabetic neuropathy is peripheral neuropathy which affects the peripheral nerves. Peripheral nerves are the nerves that exit from the brain and spinal cord to innervate the muscles, skin, internal organs, and glands. Peripheral neuropathy disturbs proper functioning of these sensory and motor nerves. The most common symptoms of neuropathy include numbness and loss of feeling, usually in the feet and hands.
Cause
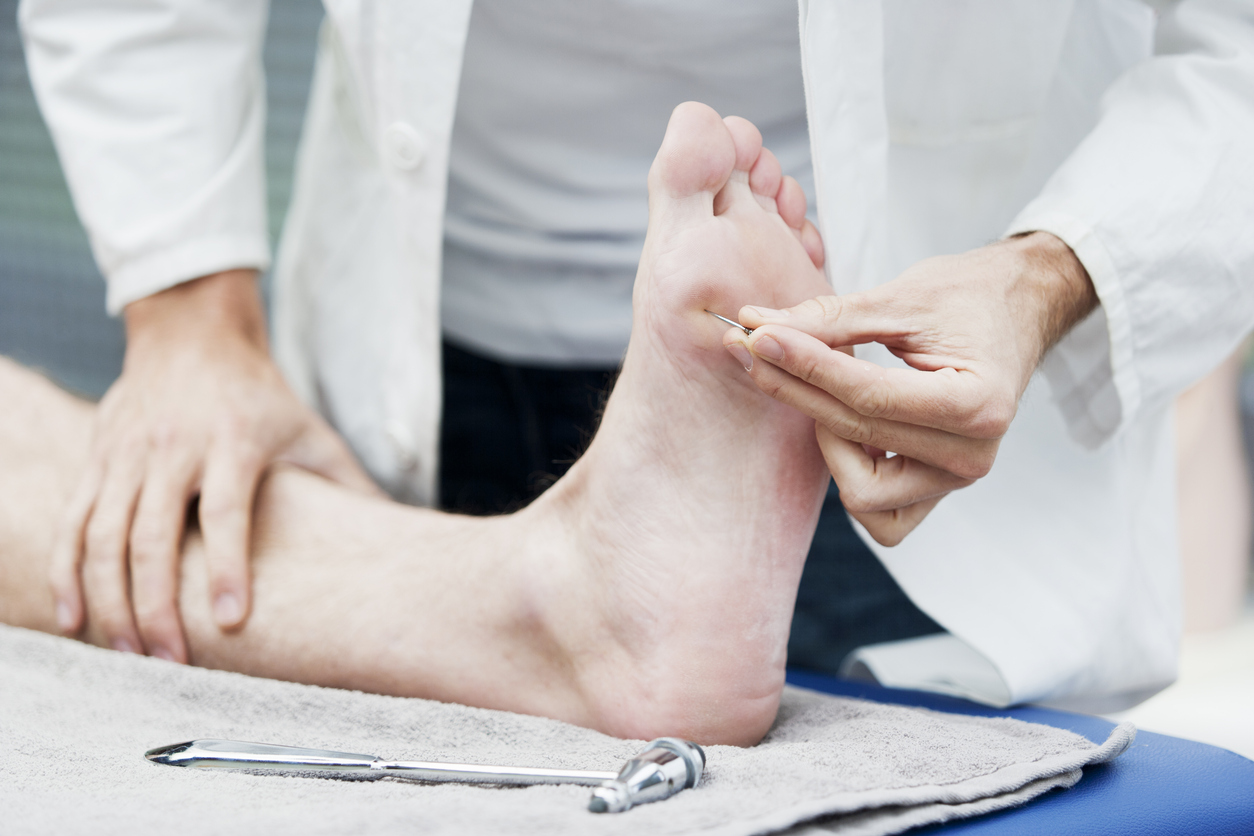
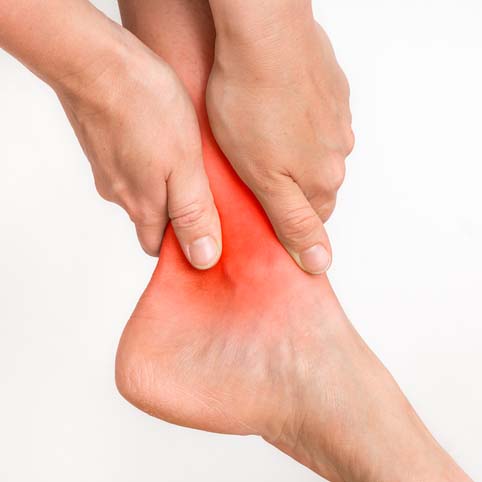
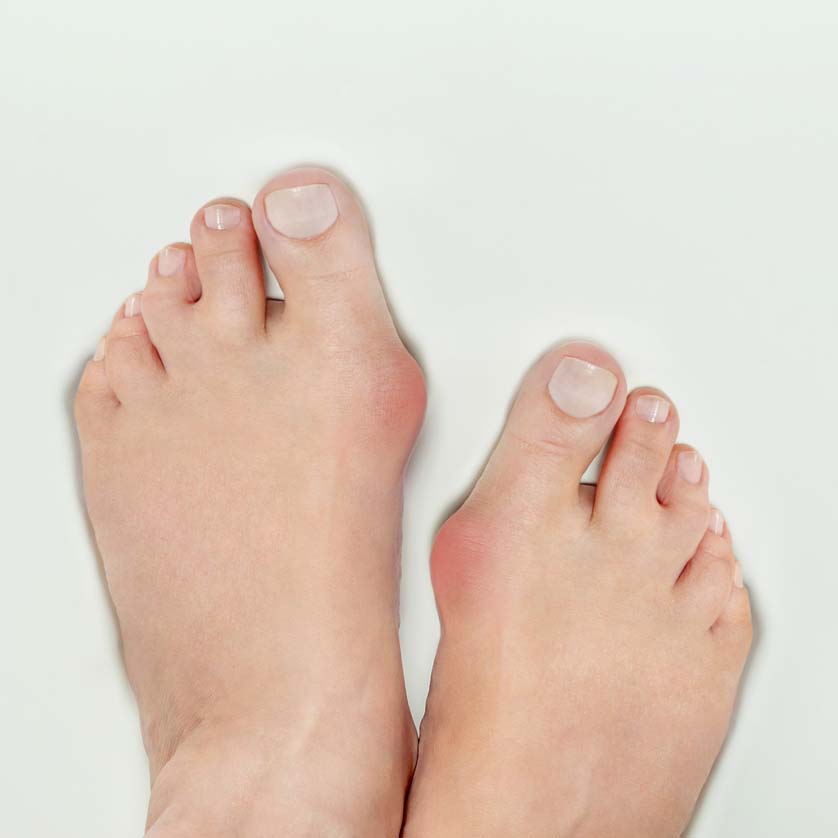
High blood sugar results in accumulation of certain metabolites and activates pathways that destroy of nerves gradually. Diabetic Neuropathy results in reduced ability to feel pain and temperature. Due to this insensitivity an individual with Diabetic neuropathy can develop minor cuts, scrapes, blisters, or pressure sores and may not be aware of it. If these minor injuries are left untreated, infections may arise and lead to ulceration and even amputation. Neuropathy also results in deformities such as Bunions, Hammer Toes, and Charcot Feet. It is very essential for diabetics to follow precautions to avoid all foot-related injuries.
Investigations
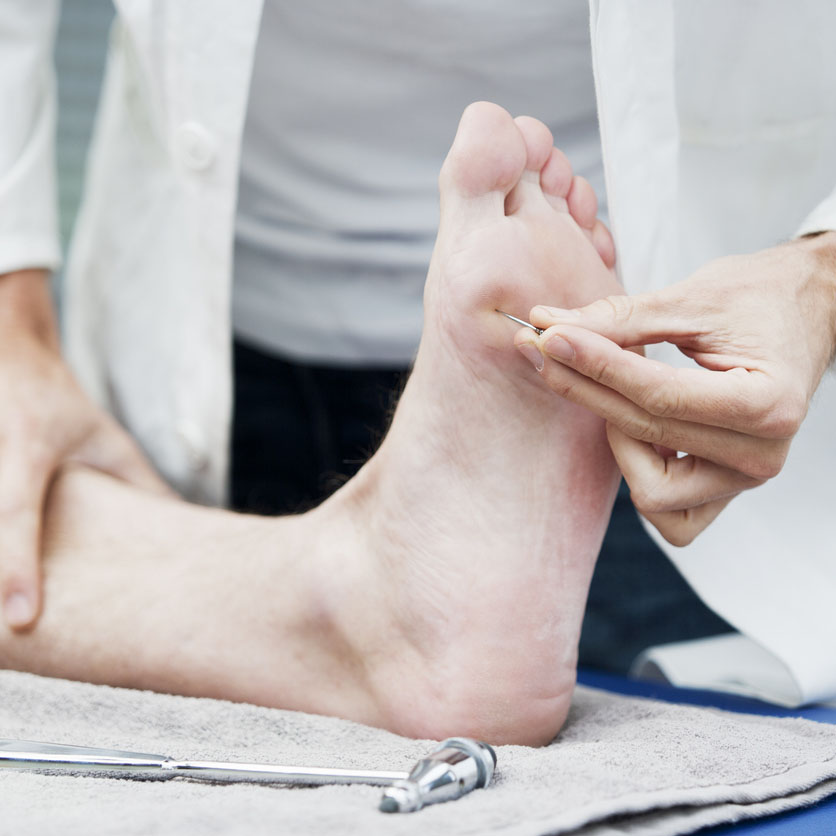
Routine blood glucose examinations and Electrodiagnosis such as Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies(NCS) helps to identify the conduction of nerves
Treatment And Prevention


The most important way to prevent diabetic neuropathy from occurring is to keep the diabetes level under control. lifestyle modifications such as Quitting habits like smoking and limit the amount of alcohol and carbonated beverages. Timely visits to diabetic clinic for regular blood and urine tests. Maintaining healthy body weight and having a balanced diet. Exercising regularly can help to utilize glucose as energy and reduce excess blood glucose. A Physiotherapist can help formulate a customized program for diabetic individual engaging in Aerobic and Strength training.
Footwear plays an essential role in diabetic foot-care. Footwear that fits poorly results in irritation and injury. Diabetic footwear should be designed as follows: Wide toe box (high and wide space in the toe area), Removable soft moulded insoles and the option to insert orthotics if necessary. Rocker soles, intended to reduce pressure in the areas of the foot most susceptible to pain, most notably the heel and metatarsals.
Read our Articles